- ABOUT JNU
- ADMISSION
-
ACADEMICS
- Schools and Colleges
-
Departments and Programs
- Arts College of
- Chinese Language and Culture College of
- Economics College of
- Electrical and Information Engineering College of
- Foreign Studies College of
- Information Science and Technology College of
- Environment School of
- Humanities School of
- International Business School
- International Studies School of
- Journalism and Communication College of
- Law School
- Liberal Arts College of
- Life Science and Technology College of
- Management School of
- Marxism School of
- Medicine School of
- Pharmacy College of
- Physical Education School of
- Science and Engineering College of
- Shenzhen Tourism College
- Research Institute
- Research Center
- Programs in English
- Majors
- Study Abroad
- Online Learning
- RESEARCH
- CAMPUS LIFE
- JOIN US
Headline News
Advanced Energy Materials publishes JNU research
Researcher Ling-tao He's team from the Institute of Science and Technology (IST), JNU, co-worked with Prof. Feng-ling Zhang of Linkoping University, Sweden, and Prof. Feng Liu of Shanghai Jiaotong University, China, published “Printed Nonfullerene Organic Solar Cells with the Highest Efficiency of 9.5%” in Wiley’s Advanced Energy Materials (Vol. 8, Issue13 May 4, 2018. IF=16.721), with the first author Yuan-bao Lin, a post-graduate of IST. Their research, also reported as one of the key items in Materials Views China, provides a new practicable method for the industrialized of large-area printed nonfullerene organic solar cells.
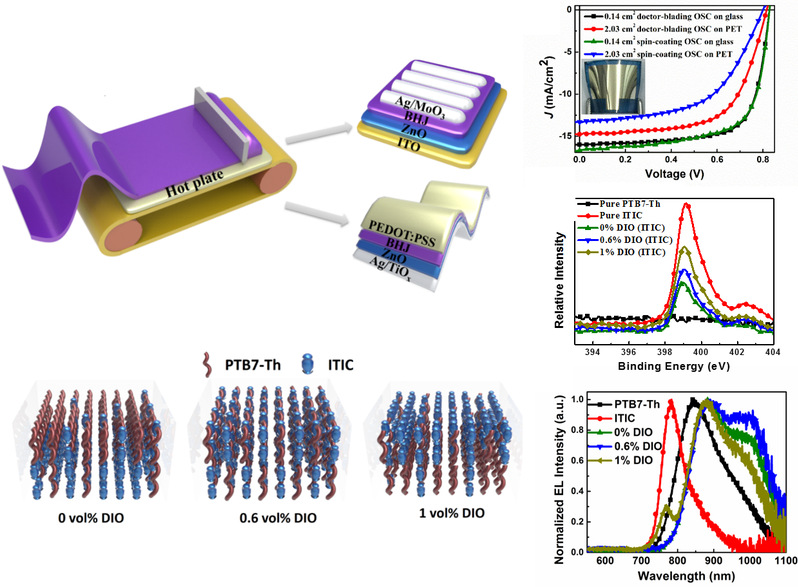
Their work reports a high power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 9.54% achieved with nonfullerene organic solar cells (OSCs) based on PTB7‐Th donor and 3,9‐bis(2‐methylene‐(3‐(1,1‐dicyanomethylene)‐indanone))‐5,5,11,11‐tetrakis(4‐hexylphenyl)‐dithieno[2,3‐d:2′,3′‐d′]‐s‐indaceno[1,2‐b:5,6‐b′]dithiophene) (ITIC) acceptor fabricated by doctor‐blade printing, which has the highest efficiency ever reported in printed nonfullerene OSCs. Furthermore, a high PCE of 7.6% is realized in flexible large‐area (2.03 cm2) indium tin oxide (ITO)‐free doctor‐bladed nonfullerene OSCs, which is higher than that (5.86%) of the spin‐coated counterpart. To understand the mechanism of the performance enhancement with doctor‐blade printing, the morphology, crystallinity, charge recombination, and transport of the active layers are investigated. These results suggest that the good performance of the doctor‐blade OSCs is attributed to a favorable nanoscale phase separation by incorporating 0.6 vol% of 1,8‐diiodooctane that prolongs the dynamic drying time of the doctor‐bladed active layer and contributes to the migration of ITIC molecules in the drying process. High PCE obtained in the flexible large‐area ITO‐free doctor‐bladed nonfullerene OSCs indicates the feasibility of doctor‐blade printing in large‐scale fullerene‐free OSC manufacturing. For the first time, the open‐circuit voltage is increased by 0.1 V when 1 vol% solvent additive is added, due to the vertical segregation of ITIC molecules during solvent evaporation.
NEWS
- About the University
- Quick Links
Copyright © 2016 Jinan University. All Rights Reserved.




